-
Resource Management and Modern Enterprise

Utilizing every resource intelligently is imperative for every organization as they are the most high-priced investments of any business. Moreover, organizations spend a lot of time and cost in creating the right talent pool. Therefore, when their skills and competencies are tapped to their maximum potential, it enhances overall efficiency and profitability.
Resource management has become an integral part of business today. It emerged as an independent discipline after organizations became complex with matrix structure and expanded in multiple geographies.
-
The importance of resource management
Resource management plays an important role in improving the profitability and sustainability of a business. Let’s focus on how enterprise resource management can help in contributing to both the top line and bottom line of any business.
1. Minimize project resource costs significantly
According to Deloitte, "Cost reduction takes precedence over other business initiatives.
With enterprise-wide visibility, resource managers can utilize cost-effective global resources from low-cost locations. Having the right mix of local and global resources helps in reducing project costs. Allocating the right resource for the right project enables them to complete the delivery within time and budget. Resource managers can control costs by distributing key resources uniformly across all projects instead of a high-priority project.
2. Improve effective/billable resource utilization
Resource management software helps managers forecast the workforce’s utilization in advance. Accordingly, resources can be mobilized from non-billable to billable and strategic work. Sometimes when resources are rolled off from projects, there isn’t any suitable work to engage them. So, eventually, these resources end up on the bench. Resource managers can initially engage these resources in non-billable work before quickly assigning them to suitable billable/strategic projects.
3. Bridge the capacity vs. demand gap proactively
Demand forecasting, a function of project resource management, allows managers to foresee the resource demand ahead of time. It enables them to assess and analyze the skills gap within the existing capacity. After identifying the shortages and excesses, resource managers can formulate an action plan to proactively bridge the capacity vs demand gap proactively.
4. Use scarce resources effectively in a matrix organization
The resource management process brings transparency in communication and hence facilitates to effectively share highly skilled resources in a matrix organization. The scarce resources can be utilized across different projects rather than one high-priority project. The shared services model will also form teams cutting across multiple geographies for 24/7 support operations.
5. Monitor and improve organization health index
Employees look up to their leaders for their professional development. Failing to motivate and provide career development opportunities will predominantly lead to reduced engagement, productivity, and unplanned attrition. Regular monitoring of their skills and performances is beneficial to help them improve and add more value to the organization.
-
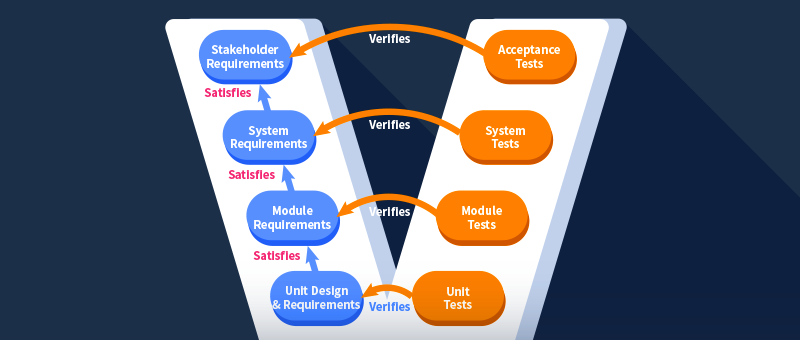
Resource Management Concepts & its Components
1. Resource scheduling
Resource scheduling involves identifying and allocating resources for a specific period to different project tasks. These tasks can be anything from billable, non-billable, or BAU work.
With a centralized Gantt chart view of the enterprise, resource scheduling eliminates silos of spreadsheets. It also facilitates you to deploy the competent resources to the right job to finish the project within budget and time.
2. Resource utilization
Resource utilization measures the amount of time spent by employees on different project tasks against their availability. It is a key performance indicator in the modern business landscape as it directly influences the firm’s bottom line.
Utilization can be measured in terms of:
- Overall resource utilization
- Billable utilization
- Strategic utilization
- Non-billable utilization
- Resource managers can proactively mobilize resources from non-billable to billable/strategic tasks and maximize their billable utilization.
3. Resource forecast
Resource forecasting helps managers predict resource utilization levels in advance and foresee the resources likely to end up on the bench. In addition to these, they can also stay forewarned of the required capacity for pipeline projects.
Using this information, managers can move resources from non-billable activities to billable tasks, ensure effective bench management, and bridge the capacity and demand gaps.
4. Resource and capacity planning
Resource planning is the comprehensive process of planning, forecasting, allocating, and utilizing the workforce most efficiently and intelligently. Resource capacity planning is an undertaking to analyze and bridge the capacity and demand gap well ahead of the curve.
These two components are vital to ensure that none of the project vacancies go unfilled or excess capacity gets wasted. Simply put, resource and capacity planning maximize optimal utilization and timely project deliveries.
5. Business intelligence and reports
Business intelligence provides actionable insights by performing extensive data analysis. Using real-time data, individualized reports, and dashboards on important resource management metrics are generated. These reports strengthen the managers’ decision-making abilities and allow them to monitor the overall resource health index.
-
Types of Businesses that Require Enterprise Resource Management?
Organizations with a matrix-based set-up, cross-functional teams, and a shared-services model require enterprise resource management. The level of complexity to which they adopt the business processes depends on their size and functions. Today resource management is part of every organization’s DNA.
Industries such as IT services, construction & engineering, audit & accounting, and professional services organizations, etc. have implemented robust resource management processes.
Other crucial factors that constitute the need for resource management are firms working on multiple projects in ad-hoc environments. It means that they are exposed to several changing variables like project priorities, resource availability, and budget constraints.
These complexities demand enterprise-wide visibility and real-time updates to help the managers stay informed at all times. They need to manage their resources diligently and finish the projects within budget and time. Therefore, organizations need to invest in resource management solutions for effectively utilizing their resources irrespective of the industry type.
Formulating a resource management framework is only half the battle won. It is equally important to implement this strategy using an appropriate resource management tool to suit organizational needs. Otherwise, poor resource management will have an adverse effect on the entire resource pool and the firm’s reputation.
-
Consequences of Poor Resource Management Strategy
1. Increased project costs
Incompetent allocation or booking of high-cost resources instead of the low-cost but similarly skilled workforce spikes project budget. Since the resources’ skills and competencies are not leveraged most effectively, project costs will increase, causing unnecessary budget overruns.
2. Reduced employee performance
Poor employee performance is the first and foremost indicator of sub-optimal resource management. Unrealistic expectations, over-allocations, or bookings without considering employee interests and skills can contribute to reduced engagement and productivity. It will adversely affect the project’s quality and lower down employee morale.
3. High employee turnover
Employees feel disengaged and dissatisfied when their strengths and skills are not exploited at their best. Over-utilization due to unrealistic deadlines can lead to employee burnout. These circumstances can compel your valued talent pool to look for opportunities elsewhere, which will gradually increase employee turnover.
4. Delays in meeting project deadlines
Without visibility of team members and their skill sets, resources may get allocated to projects that do not match their competencies. It can result in delivery delays as significant time will be spent learning on the job before becoming productive. Delays in meeting deadlines also blow up project costs.
5. Client dissatisfaction and loss of business
Inefficient resource management practices lead to poor resource allocation, which causes teams to put in longer hours for meeting project goals. Tight deadlines and a heavy workload can put the team under pressure, thereby increasing the likelihood of errors. Delayed delivery, compromised quality, and budget spike jeopardize project health resulting in client dissatisfaction and eventually business loss.
The main part of this article comes from the following link:https://www.saviom.com/blog/what-is-resource-management/


 is cool!
is cool! provides you a comprehensive
picture of recent, current, and likely future of your infrastructure and operations.
provides you a comprehensive
picture of recent, current, and likely future of your infrastructure and operations.