-
Transparent execution
Execution is the single greatest market differentiator. Great companies execute better than their competition.” While this may seem like common sense, many companies fail to execute effectively. In fact, it's been estimated 60-70% of business strategies are not successfully implemented.
-
Most project management tools on the market are only good for creating a project plan, but not for executing a project
The first popular project management tool was a document preparation tool for creating project plans It was released together with other document preparation tools for creating electronic spreadsheets and electronic presentations. These tools were designed for creating documents in specific formats. But they are far from a real-time trading, bidding or betting system in terms of their capabilities of managing multiparty real-time execution and protecting data integrity dynamically.
People often lie in project environments because their project management systems allow them to do so. People don’t lie in banks’ trade settlements or jockey clubs’ payouts because their systems don’t allow them to do so.
For multiparty transaction and data integrity projection standpoint, the current project management tools on the market are more inferior to Automated Teller Machine (ATM) systems that were first introduced in 1969. Of course, there are ways of designing a project management tool to make it useful for project execution.
-
How reliable is project management information today without a transaction oriented data model?

The difficulty of project management coming from the unreliability of project management information triggering and promoting human’s dishonesty. Exactly how unreliable is project management information? PMP students often learn from their instructors that a project can make artificial progress such as 50% -> 60% -> 70% ->80% -> 90% complete and then suddenly come back down to 50% complete even with no major changes in requirements. This tells you that the project progress can lie on top of lies until everyone knows that no one can say the project is 100% complete or the project will need to be actually finished.
If you closely examine the commonly used project management tools, you will find the computerized transaction is the entire project plan document and no traceability of how and when plan B, C and D were merged into plan A. As a result, things similar to what is described in the diagram below happen.

-
How reliable is project management information using ?
The reliability (transparency and incorruptibility) of the
 data storage model is the key in solving the problem mentioned above. From data reliability standpoint, using
data storage model is the key in solving the problem mentioned above. From data reliability standpoint, using  for project activities is very similar to using a CDM/ATM which has the current status or balance and incorruptible past interaction and transaction records.
for project activities is very similar to using a CDM/ATM which has the current status or balance and incorruptible past interaction and transaction records.

 ’s Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) can also track every single project activity or deliverable associated with the audit trail. It also displays a single view of accurate plan & execution information to everyone in real-time to totally eliminate the misperception caused by multiple versions of the truth.
’s Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) can also track every single project activity or deliverable associated with the audit trail. It also displays a single view of accurate plan & execution information to everyone in real-time to totally eliminate the misperception caused by multiple versions of the truth.
The high reliability of project management information in
 keeps people honest which is the essence of management
keeps people honest which is the essence of management
-
Project plan and execution are inseparable (always linked together by the system)
If plan and execution do not go hand in hand, unnecessary complications, such as the following, will need to be managed manually to maintain a valid plan to guide the team:
a) Manual checks will be necessary to ensure that no one forgets to update the changed dates and dependencies of his deliverables
b) Manual checks will be necessary to ensure that no one forgets to submit his deliverables for review as required
c) Manual checks will be necessary to ensure that no one forgets to review the deliverables that they are supposed to review
And a project can easily have hundreds, thousands or even tens of thousands of dates, dependencies and deliverables and it is asking for trouble if plans and execution results are automatically linked by the system.
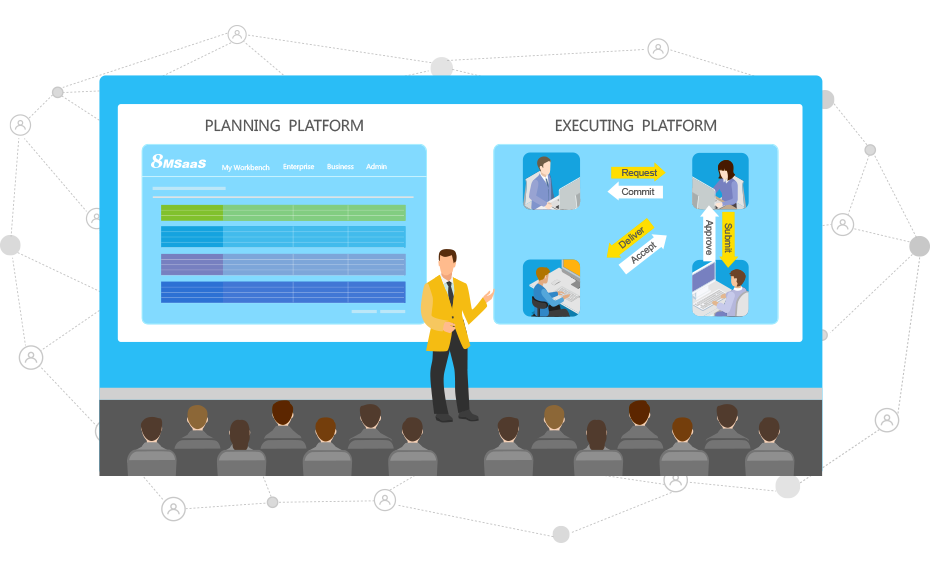
Another symptom of disconnect between plan and execution is “multiple plans”. “Multiple plans” cause serious accountability issues since each team member will follow the version of plan that is closest to their own deliverable status; but that does not help the team to function in an orderly manner.
In
 , plan and execution are inseparable and there is always one and only one current plan that everyone shares.
, plan and execution are inseparable and there is always one and only one current plan that everyone shares.
-
Scope and communications are managed together
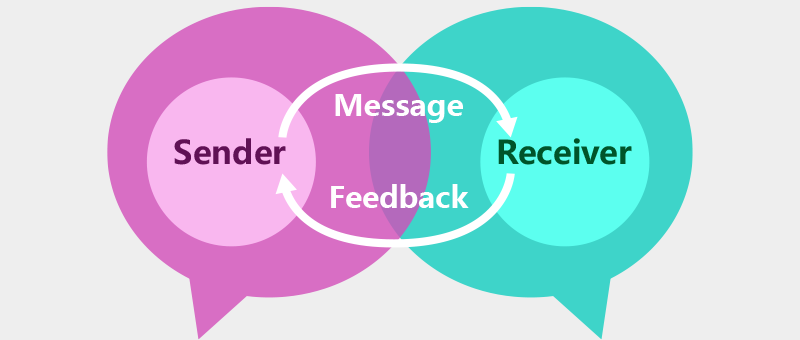
Because of human limitations, it is often difficult to communicate requirements in a single exchange (as stated on the left).
 fosters an iterative approach to delivery and acceptance of requirements. By using
fosters an iterative approach to delivery and acceptance of requirements. By using  to plan requirement deliverables, people are encouraged to start early and plan multiple iterations of exchanges. This allows more time to deal with mental transfer of requirements and the planned multiple iterations will encourage discipline.
to plan requirement deliverables, people are encouraged to start early and plan multiple iterations of exchanges. This allows more time to deal with mental transfer of requirements and the planned multiple iterations will encourage discipline.

 provides Reality Check (which is an on-demand real-time questionnaire service) to detect human communication disconnects as stated on the left. The awareness of such disconnect will help both sides find ways to improve.
provides Reality Check (which is an on-demand real-time questionnaire service) to detect human communication disconnects as stated on the left. The awareness of such disconnect will help both sides find ways to improve.
Human communication is a complex and imperfect process.
 compensates for such inadequacy by encouraging early dialogue; injecting discipline; and detecting problems at the earliest possible time so that the participants involved will have time to express themselves properly.
compensates for such inadequacy by encouraging early dialogue; injecting discipline; and detecting problems at the earliest possible time so that the participants involved will have time to express themselves properly.
-
Accountability and results are clear and transactional (recorded with incorruptible data)
Having the name of a person next to a deliverable with a due date in a project plan does not automatically equate to a firm commitment from the person. Accountability and commitment should be clear and explicit. When a commitment and result will affect deliverables from multiple people, then the commitment and result must be visible to all the people concerned.
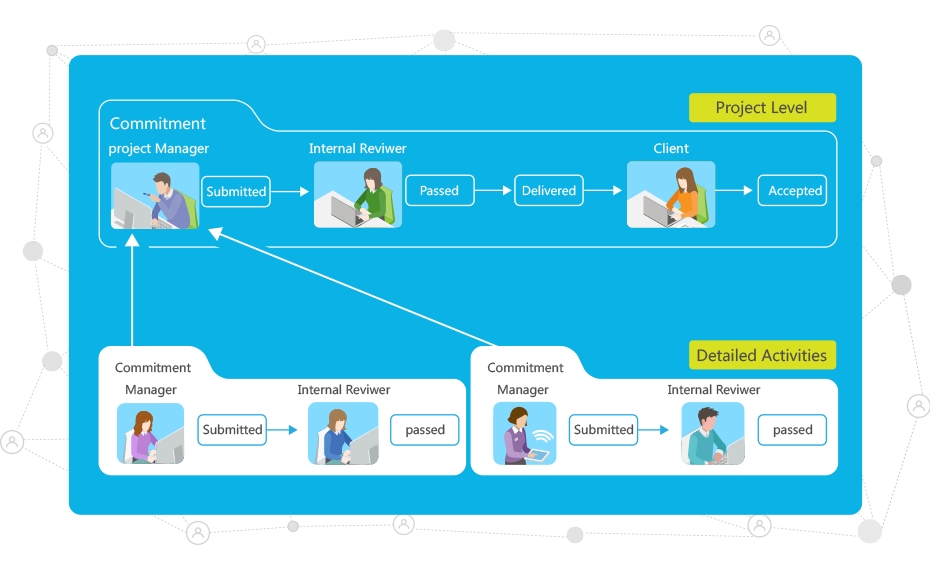
 helps to structure work in a natural manner where proper accountability and commitment will be enforced. When someone changes her commitment,
helps to structure work in a natural manner where proper accountability and commitment will be enforced. When someone changes her commitment,  will notify the affected parties.
will notify the affected parties.  also provides dashboard notification to warn people of possible over-commitment and helps people to understand the risks for a vague commitment (where one does not really know what one is committing to or the degree of difficulty of the effort) and of over-commitment. These occurrences do not help the individuals or the project as a whole.
also provides dashboard notification to warn people of possible over-commitment and helps people to understand the risks for a vague commitment (where one does not really know what one is committing to or the degree of difficulty of the effort) and of over-commitment. These occurrences do not help the individuals or the project as a whole.
Clear results (whether a deliverable is accepted or not) is very important for enforcing proper accountability. Poor end results are often caused by the unclear measure of immediate results.
 provides the following to facilitate result management:
provides the following to facilitate result management:
- Setting digital policies for review and acceptance
- Real-time alerts for review and acceptance results
- Real-time dashboards and periodical email of reports
-
Accountability and results can be made clear to all stakeholders by using the above features in
 .
.
-
Resource needs and dependencies are clear and explicit
 helps project team members to manage this complexity by:
helps project team members to manage this complexity by:
a) Making the resource and deliverable dependencies as explicit as possible
b) Automatically tracking indirect dependencies
c) Automatically detecting bad dependencies and warning people as needed (i.e., a deliverable being late that will cause other deliverables to be late)
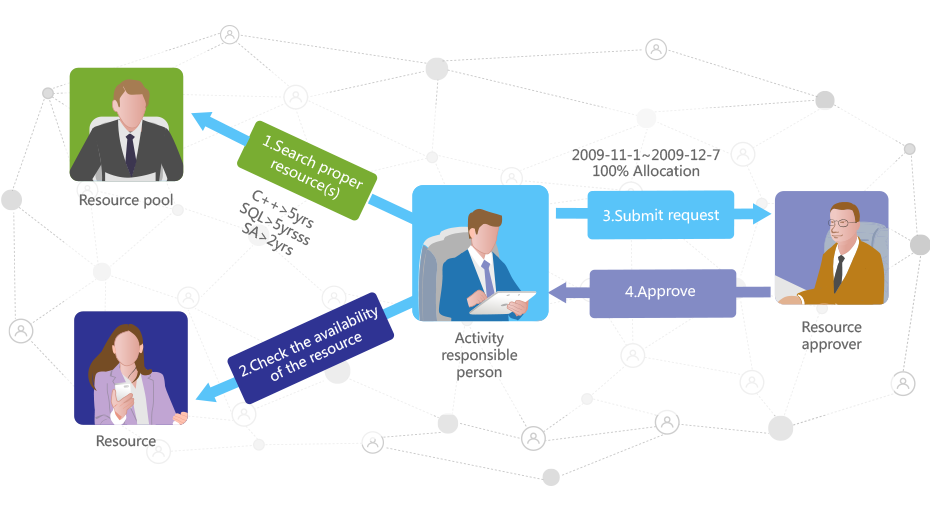
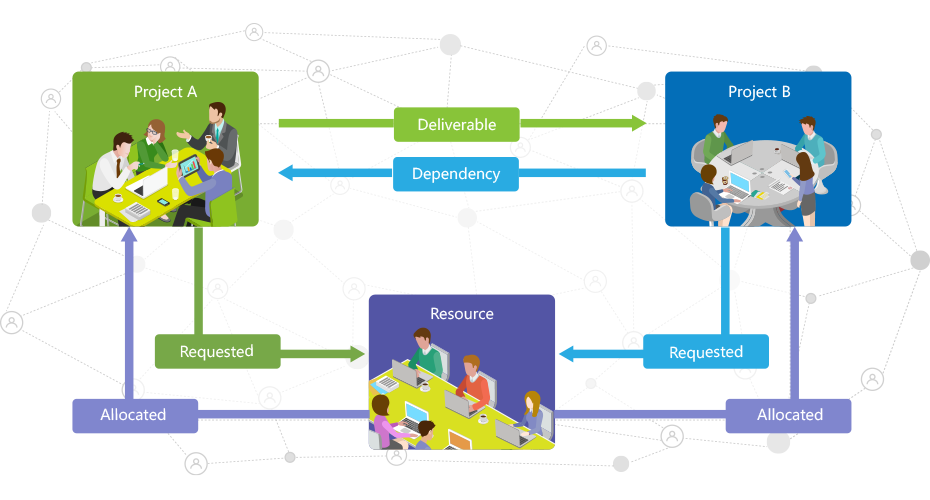
Resource sharing and dependencies can increase the complexity of managing a project tremendously. For economic reasons and because of the scarcity of expertise, resources are often shared. Work breakdowns make dependency issues unavoidable in almost any project.
-
Power to access to and manage more external resources
 can extend your access to multiple sources of talents that aren’t not under your control. By using
can extend your access to multiple sources of talents that aren’t not under your control. By using  Open Request function, you can even let the suitable talents come and find you.
Open Request function, you can even let the suitable talents come and find you.
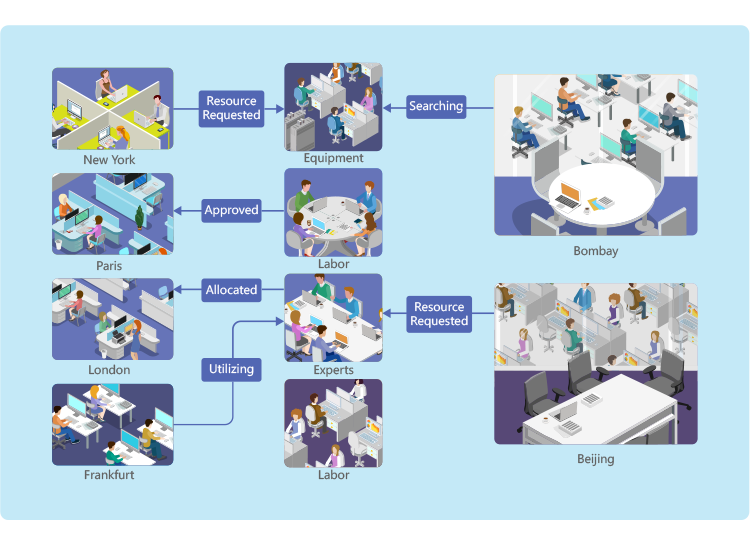
 also allows you to define digital rules how the deliverables will be reviewed and accepted and how the resources will be paid. Being able to improve your access and management of external resources will help run your projects more effectively.
also allows you to define digital rules how the deliverables will be reviewed and accepted and how the resources will be paid. Being able to improve your access and management of external resources will help run your projects more effectively.
-
Issues and risks are automatically tracked and escalated
Issues and risks can complicate a project. If not managed well, they can even halt a project.
 provides a framework to manage project issues and risks in an orderly manner to reduce complexity.
provides a framework to manage project issues and risks in an orderly manner to reduce complexity.
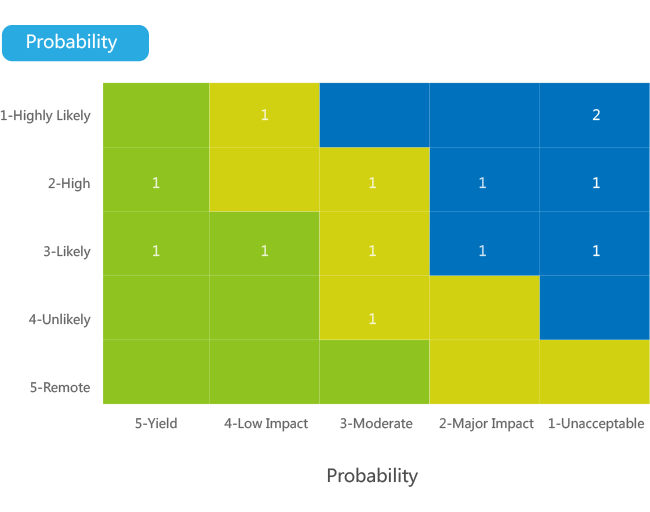
Managing issues and risks by itself is complex. An issue can be one of the following:
- 1. a non-issue (e.g., just somebody’s misunderstanding)
- 2. a defect report
- 3. a change request
- 4. a needed action
- 5. a risk
An issue can also be associated with a resource, a deliverable, a lower level activity, a higher level activity or a project.
A risk can have:
- Negative impact
- Positive impact
A risk can have different levels of probability (remote to highly likely), a different priority (yield to unacceptable) and different types of methods (avoid, transfer, mitigate, accept) to manage it.
The aggregated view of issues and their resolutions is also needed in order to manage issues in an orderly manner.
-
Performance can be observed in real-time
A deliverable or milestone is late only one day at a time. When a project suddenly slips its schedule by several weeks because the problem or lateness wasn’t detected at the earliest possible time. When the project plan and the project execution are inseparable, deviation can be detected at the earliest possible time. When the deliverable and its associated responsibilities are tracked together by the system, people’s performance problems can also be detected at the same time.
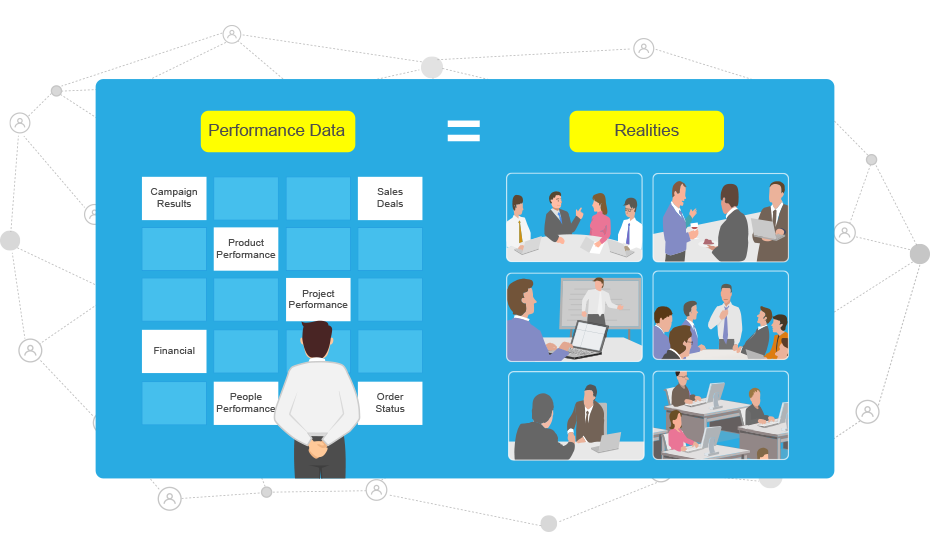
Being able to keep people honest, eliminate excuses and manage people’s performance effectively perhaps is the most IMPORTANT feature of project management tools.
-
Best practices are both encouraged and enforced with digital rules
Traditionally, standards and best practices are documented on papers. Because different people interpret them differently, or misunderstand them, standards and best practices are often empty statements for political purposes. They are often disregarded, not followed to improve project results.
 provides a Project Template facility to allow the defining of best practices, and the Policy facility to encourage and enforce best practices during execution.
provides a Project Template facility to allow the defining of best practices, and the Policy facility to encourage and enforce best practices during execution.
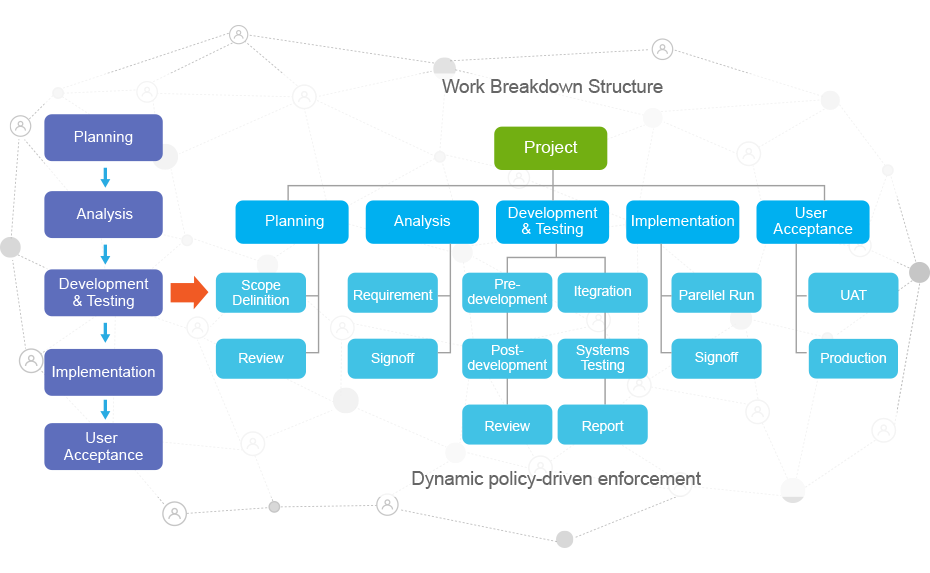
Due to the fact that a static view and a dynamic view are often different, during project execution, people often find certain needed controls lacking and certain procedures unnecessarily clumsy; consequently adjustment to the policies is needed.
 allows the governance body to adjust the policies to enable project execution to continue.
allows the governance body to adjust the policies to enable project execution to continue.
Without the integration of the static and dynamic views, standards and best practices often look good on paper but are not practical. The traditional way of solving the problems is by adding policies and making the standard and best practices document thick and impossible to read, and impossible to carry out such instructions during execution.
 solves this problem by beautifully reducing complexity, allowing people to see both static and dynamic views and to make adjustments incrementally.
solves this problem by beautifully reducing complexity, allowing people to see both static and dynamic views and to make adjustments incrementally.


 is cool!
is cool! provides you a comprehensive
picture of recent, current, and likely future of your infrastructure and operations.
provides you a comprehensive
picture of recent, current, and likely future of your infrastructure and operations.