Special News
Mastering Supplier Management: Key Challenges and How to Solve Them
2024-07-31
Supplier management is crucial in the modern business environment and is an essential part of procurement activities. Procurement organizations must ensure their suppliers are properly managed to maintain successful working relationships. However, managing suppliers can be a daunting and challenging task. Here are some common challenges procurement organizations face and effective solutions.
1. Establishing Good Relationships with Suppliers
Building and maintaining positive relationships with suppliers can be difficult, especially when dealing with numerous suppliers simultaneously. Key elements for establishing good supplier relationships include communication and collaboration, building mutual trust, and mutual growth. Through timely, clear, and effective communication, both parties can understand each others needs and expectations and work together to resolve issues. Building mutual trust is based on honest, transparent, and reliable cooperation, which fosters supplier trust in your organization. Lastly, mutual growth means both parties work together to achieve long-term cooperative success, sharing opportunities for profit and innovation to establish sustainable partnerships.

2. Controlling Supplier Performance
Real-time control of supplier performance is another common challenge. Key steps in supplier performance management include setting clear performance indicators, establishing contracts and agreements, monitoring and measuring performance, creating feedback and communication mechanisms, developing improvement plans, and seeking continuous improvement. These steps enable effective evaluation and control of supplier performance, ensuring smooth operation and continuous improvement of the supply chain to meet customer needs and expectations.
3. Ensuring Supplier Quality
In addition to collaborating with suppliers to meet product quality standards, supplier management continually strives to identify and implement business process improvements that directly impact operational efficiency and the bottom line. Typical quality issues supplier management must address include improving the efficiency of production management processes, avoiding defects in materials and packaging, and managing and reducing supplier incidents and problems.
4. Reducing Procurement Risks
From environmental and public health issues like natural disasters and pandemics to events like trade wars, there are numerous risks threatening supply chain disruptions. These include risks such as raw material shortages, price fluctuations, and lack of upstream supply chain visibility. Successfully collaborating with suppliers and reducing risks is a key responsibility of the supplier management team. This involves establishing supplier diversification and qualification evaluation mechanisms to ensure supply chain transparency and reliability; drafting clear procurement contracts and terms to define both parties rights and responsibilities; implementing supplier performance monitoring and evaluation to identify and resolve potential risks promptly; fostering close partnerships to enhance communication and information sharing; and actively monitoring market changes and supply chain risks to adjust procurement strategies promptly. These measures can reduce procurement risks and improve procurement success rates and efficiency.
Supplier Management Software Solutions
In todays information technology era, technology can facilitate trustworthy relationships between buyers and suppliers. Supplier management software allows buyers to share data with suppliers. Besides helping companies source goods at reasonable prices, supplier management software can guide companies to improve their relationships with suppliers.
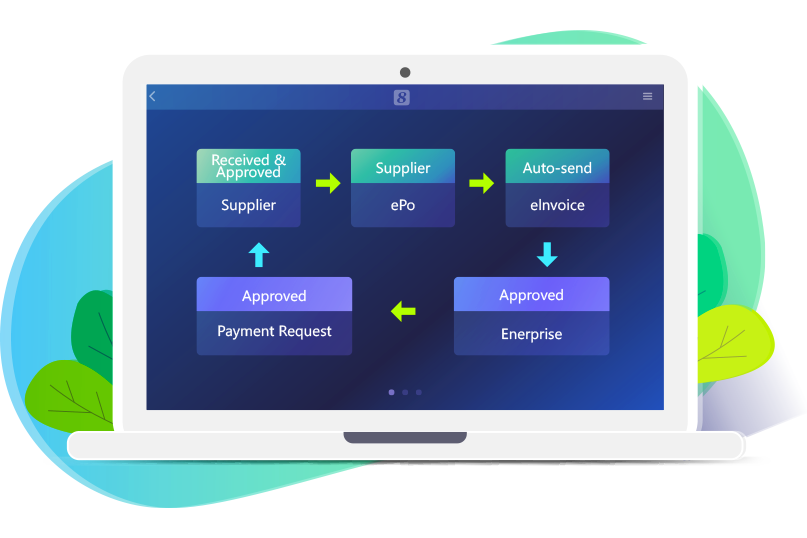
8Manage SRM supplier management software helps procurement organizations effectively track supplier performance and manage supplier relationships, enabling quicker, more informed decision-making and improving productivity, quality, and continuous improvement. As an end-to-end solution, 8Manage SRM offers numerous features for managing buyer-supplier relationships:
Supplier Access: Adding suppliers to an approved list with all necessary documentation and data.
Supplier Identification: Screening suitable suppliers based on quotes received during the inquiry and tender process.
Supplier Selection and Segmentation: Determining suppliers based on various indicators such as lifecycle cost, quality, time, availability, transaction volume, dependency, maintenance and support costs, compliance, etc.
Supplier Performance Management: Measuring and analyzing supplier performance throughout the contract term to identify weaknesses and mitigate supplier risks.
Supplier Information Management: Collecting information at every step of the supplier lifecycle, from onboarding to formal exit, covering aspects related to risk management, continuous contract fulfillment, and more.
Supplier Risk Management: Identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks within the supplier database. This requires actively monitoring all new and existing suppliers and developing effective risk contingency plans to prevent major supply chain disruptions.
Supplier Relationship Management: Identifying the most strategic suppliers and establishing long-term relationships, which is a best practice in procurement.
Additionally, 8Manage SRM includes modules for inquiries and comparisons, bidding, tendering, and procurement process control, providing a comprehensive solution for supplier and procurement management. This helps enterprises optimize supply chain management, reduce risks, and improve efficiency and quality.
Conclusion
Supplier management is a critical part of an enterprise. In todays highly competitive market, companies that do not invest in supplier management often incur higher costs. With the help of the 8Manage SRM system, enterprises can compare and select suppliers based on factors such as price, past performance, or a combination of both. Building strong supplier partnerships can help companies maintain a leading position and competitive advantage.
Most popular

How IPD drives product R&D toward commercial success

Top procurement management systems to elevate your business in 2025

Are your project managers ready for AI?
Related articles
How to choose the best procurement management software for your business?
2025-03-07
Top 5 procurement and tender management systems in 2025: Rankings and reviews
2025-03-05
Top 6 procurement management software for businesses in Hong Kong
2025-02-26
Real estate procurement management system selection guide
2025-02-13
2025 Guide to supplier management systems for manufacturers
2025-01-24
Previous Article >
Choosing a Top Procurement Software Solution: 8Manage SRM
Choosing a Top Procurement Software Solution: 8Manage SRM